Heart attack symptoms
Introduction
Heart attack symptoms are signals that should be given particular attention; they represent the alarms that a heart is suffering. Early intervention is critical when such signs are noticeable in an individual or a killed person’s body. A myocardial infarction or heart attack is a condition where the blood supply to any area of the heart muscle is restricted, causing the death or damage of the part of the muscle. Early recognition of the symptoms of the heart attack is easily the difference between living and dying. The symptoms might be even different in different people, and harsh symptoms seen in movies may not be the same all the time. In some cases, the symptoms of a heart attack might be very mild, and that would make it difficult to tell when the heart attack has started. All the people must be aware of many signs that a person can have a heart attack to increase the chances of saving people’s lives and providing overall care.
Common heart attack symptoms: what to look for

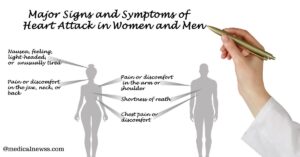
Some of the signs of heart attacks are chest pains, discomfort, or pressure. This sensation is common and can be described or felt as tightness or fullness in the chest. This may also be felt in the arms, neck, jaw, or back, which are typical signs commonly associated with heart attacks. Another early sign of a heart attack is discomfort in the chest area, and shortness of breath is the other sign. It can be with chest pain or without chest pain, and hence it should not be overlooked in any way. Sometimes tones of the indicators of a heart attack can include sweating, nausea, dizziness, or lightheadedness. Though such problems are often accompanied by other illnesses, individual symptoms mentioned above should alert immediately in case they are combined. By understanding these symptoms, most people will be able to make the necessary arrangements of being rushed to the hospital in cases of heart attacks.
Common Heart Attack Symptoms: Identifying Symptoms While Implementing Management of Urgent Skin care efficiently.
Unusual Heart Attack Symptoms in Women
The symptoms of a heart attack in women are not always quite similar to the symptoms seen in men. Chest pain is typical, but women can have vague signs of a heart attack that may be mixed up with other illnesses. For example, it is established that women feel more pain or discomfort in other aspects apart from the chest, in the stomach, back, shoulders, or even the upper abdomen. However, nucleuses, nausea, dizziness, and lightheadedness are reported to occur more often in women. Women also tend to complain of shortness of breath and fatigue—signs that can easily be mistaken for stress or anxiety. Since the signs of heart attacks in women can sometimes be not as obvious as in men, every woman should know these signs and get help immediately. Such awareness results in early participation and better results.
Silent Heart Attack Symptoms: What You Need to Know
In fact, not all heart attacks present themselves in grand style or with very apparent signs. Symptomatic silent heart attacks are a major problem because the symptoms often do not manifest themselves for several hours. These are not the drastic symptoms most people associate with a heart attack and can include tireness, discomfort, or slight chest pains. Most of the time, the individuals experiencing the symptoms can easily be attributed to getting a stomach ache or muscular strain. The fact that heart attack symptoms may not manifest themselves externally makes it even more important to control such factors as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, or a strong family history of the disease. Major ones may not result in permanent change of the heart muscle when they are diagnosed early, but they are dangerous since they could progress to cause other problems at a later date. Any person with this condition should always be very cautious with their overall health and always check some signs and symptoms of heart disorders, even if they believe those signs are trivial.
Pain and Discomfort as Heart Attack Symptoms
Pain in the chest is one of the best recognized symptoms of a heart attack and a symptom that is quite famous. The pain is said to originate from the chest area and can spread to other regions of the body, including the left arm, neck, back, jaw, or even the abdomen. This discomfort is normally viewed as a pressure, a feeling of fullness, or an odor of tightness. It may be sore and can sometimes even be stab-like in nature, or it can be a constant throbbing pain. Whether the pain is sharp, dull, burning, shooting, or even slight, every pain that occurs suddenly or becomes severe or lasts for more than 5 minutes requires attention. At times the signs of a heart attack may be similar to other conditions like heartburn, but in the case of a heart attack, there are likely to be related symptoms like shortness of breath, excessive sweating, or dizziness. Soon enough, medical attention can be sought so as to avoid more damage to the heart and a better prognosis.
Breathing Difficulties: A Critical Heart Attack Symptom
Breathlessness is another acknowledged sign of a heart attack that is often accompanied by chest pain. As a rule, a number of patients who have a heart attack may experience severe, effortless shortness of breath in other situations that do not require exertion. This symptom is normally accompanied by chest constriction or a feeling of choking. Often enough, the breathing distress might be mistaken for a panic disorder or asthma, which makes diagnosis challenging. Pain related to a heart attack and accompanied by shortness of breath most commonly develop rapidly and intensify. If a person feels breathless and he doesn’t know why he feels that way, particularly if this is accompanied by chest pain and dizziness, the patient should go to the doctor urgently. Lost blood flow to the heart’s tissues can be recovered, and the more potent consequences of an attack can be averted if aid is sought initially.
Heart attack symptoms: nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting are among the symptoms of a heart attack that are not so often mentioned; nevertheless, they should not be disregarded. In fact, it is not uncommon for those having a heart attack, particularly women, to complain of nausea or vomiting before the event. This symptom is usually paired with feelings of gastrointestinal upset or a kind of she-better-not-touch-me discomfort. Why nausea occurs in the course of myocardial infarction, to this very day, remains unclear, though it is attributed to autonomic nervous system responses to pain from the myocardial infarction event. If nausea is felt together with other signs such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness, all these should be considered as indications of a heart attack, and emergency intervention is required. This shows that regular and early treatment could have sufficiently reduced the impact on the heart as well as the overall chance of survival.
Dizziness and Lightheadedness: Heart Attack Symptoms to Watch For
Fainting and lightheadedness are unnoticed but are part of the signs and symptoms of a heart attack. Such sensations are possible because the brain, for a moment, does not receive blood with oxygen due to the inefficient pumping of the heart. Pre-syncope patients may also describe dizziness that, at a stage of heart attack, resembles a feeling of turning weak, light-headedness. This could, however, be followed by sweating, confusion, or feeling generally weak. But one must understand that dizziness as a symptom, together with chest pain, shortness of breath, or nausea, should not be endured or ignored. If these signs occur, then it might indicate a serious cardiovascular event, and hence an urgent trip to the hospital is necessary. Many people do not pay attention to the signal of dizziness and thus make the detection of a heart attack rarely early, thus causing serious complications.
Jawache and Other Half-Signs of a Heart Attack
Pain in the jaw is one of the least appreciated signs of a heart attack, but the sign is very important for women. It may be located in the lower jaw, teeth, or the region of the divide of the jaw, and maybe present from the onset or progress over a few days. He or she connects it with chest, neck, or arm pain that is usually mild to moderate for most sufferers. It is often confused with a dental problem, but it is a signal of a heart problem too—a heart attack, to be precise. This symptom is usually accompanied by the other essence of a heart attack, such as short breathlessness, vomiting, and fainting. Jaw pain should be considered as one of the symptoms of a heart attack to avoid cases whereby a person will be diagnosed late to warrant emergency surgeries that would minimize the possibility of a permanently damaged heart.
Fatigue: An Often Overlooked Heart Attack Symptom
Another sign of a heart attack that a lot of people do not recognize is fatigue. This feeling of utter fatigue may begin abruptly or pass gradually and may be associated with other symptoms such as weakness or breathing problems. In more severe cases, it may be impossible to go without sleep for even one night because exhaustion is so disabling that it makes it difficult to walk or climb stairs. The signs of fatigue prevailing a heart attack can hardly be distinguished from stress, poor night’s sleep, or other insignificant health issues. Nevertheless, if the fatigue is accompanied by chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness, it should not be disregarded. Persons who suddenly feel tired they cannot explain, particularly if the tiredness worsens or becomes associated with the following: Chest discomfort, shortness of breath, cold sweats, or severe pain in the arms, neck, back, abdomen, or jaw should rush to a doctor as they may be having a heart attack or another cardiovascular emergency.
Recognizing Heart Attack Symptoms in the Elderly
Recognizing Heart Attack Symptoms in the Elderly Heart attack symptoms in the elderly may not always follow the typical pattern seen in younger individuals. Older adults are more likely to experience atypical heart attack symptoms, which may include confusion, shortness of breath, fainting, or sudden weakness. They may not always feel the intense chest pain that is commonly associated with a heart attack, and as a result, they may delay seeking help. Given that heart disease is more common in the elderly, it is essential for caregivers and family members to be aware of these potential signs. If an elderly person shows signs of fatigue, confusion, or unexplained pain in the chest or elsewhere, immediate medical attention is crucial. Recognizing heart attack symptoms early can improve the chances of recovery and prevent further complications.
Prevention and Treatment of Heart Attack Symptoms
Prevention is equally important in reducing the risk of a heart attack. Maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress can significantly lower the chances of experiencing heart attack symptoms. Additionally, monitoring and controlling risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes is essential. Individuals at high risk can use medications or lifestyle changes to manage these factors. Once heart attack symptoms occur, prompt medical treatment is necessary. The earlier treatment is administered, the better the chances of minimizing heart damage and improving recovery outcomes. Emergency interventions like clot-busting drugs, angioplasty, or bypass surgery may be necessary to restore blood flow to the heart.
Conclusion
Signs of a heart attack should not be ignored at any cost. Knowledge and appreciation of these signs are critical in the early presentation of medical symptoms that may compromise the heart and its function. All discomforts, including chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, dizziness, and less frequent symptoms, including jaw pain and fatigue, should elicit a response. Chest pain or discomfort are perhaps the most common sign of a heart attack, although there is never a single way that the disease can manifest itself, so the main thing is to remain vigilant about the signals the body sends to the mind and to call the doctor in case of any odd or prolonged discomfort. They can also prevent other conditions through tender preventive measures, including working to improve the overall health of the heart. Therefore, if the population is aware and alert, there is a high likelihood that they will improve.