Hepatic Parenchymal Disease
Introduction
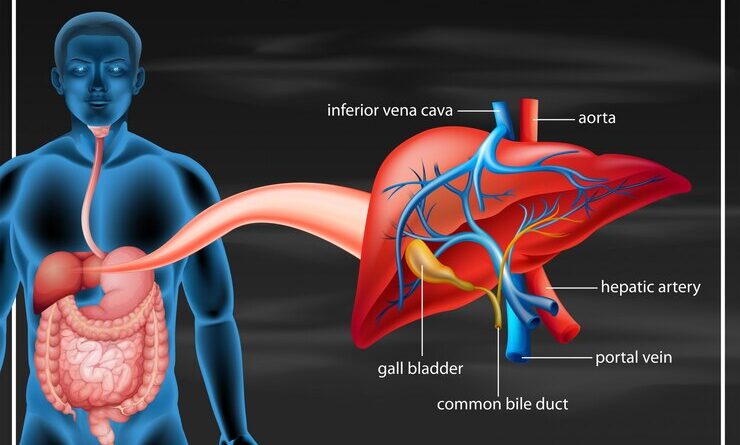
Hepatic parenchymal disease is the term used to denote various conditions affecting the liver, including diseases of its actual tissue—the parenchyma. It is with the help of this tissue that such important hepatic functions as detoxification, protein synthesis, and the formation of chemicals required for digestion are realized. So, hepatic parenchymal damage may lead to serious pathologies, such as hepatic inflammation, fibrosis, and even cirrhosis. Hepatic parenchymal disease is a very important consideration in relation to the whole health of the human body. This article will help us know the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options.
Causes of Hepatic Parenchymal Disease
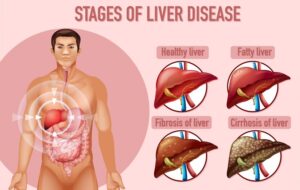
Digestive Health in Tupelo, MS: Find out about the causes of Hepatic Parenchymal Disease and how to handle the situation. Several factors can cause damage to the liver tissue and result in hepatic parenchymal disease. The major causes include chronic alcohol consumption, viral hepatitis (like hepatitis B and C), and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Alcohol-related liver disease is one of the most common reasons; long-term abuse of alcohol usually and invariably results in liver inflammation and scarring. In this case, particularly in the absence of proper treatment, chronic active hepatitis of viral etiology produces chronic inflammation that leads to fibrosis and cirrhosis. In the case of NAFLD, fat will be deposited within the liver, resulting in inflammation.
Symptoms of Hepatic Parenchymal Disease
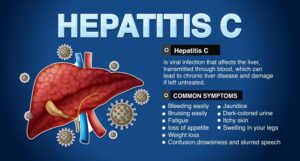
The symptoms of parenchymal hepatic disease are also dependent on how severe it may be. One has mild symptoms of fatigue, weakness, and unexplained weight loss at the onset of the disease. The unilateral advanced disease results in more serious associated features that include jaundice, abdominal pain, swelling in the legs, and in the abdomen with dark urine. Different side effects might incorporate disarray or memory breakdowns, by which the liver neglects to clean the blood. Early awareness of such signs should trigger one to seek medical attention in time.
Diagnosis of Hepatic Parenchymal Disease

Diagnosis of hepatic parenchymal disease entails medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Blood tests determine the level of liver functions, enzymes, bilirubin, and other markers. Imaging, mostly through ultrasound, CT, and MRI, may provide a clear image of the liver, which further helps the doctors check the injury extent on the hepatic parenchyma. Sometimes, your doctor may decide on a liver postmortem in the interest of obtaining a small tissue instance for microscopic examination. Early diagnosis is very important for trying to prevent more liver damage and for treating hepatic parenchymal disease.
Treatment Options for Hepatic Parenchymal Disease
In cases of viral hepatitis, antiviral drugs would be given in order to treat the infection and reduce the inflammation that might have occurred in the liver. In cases of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, lifestyle changes, including proper dieting and exercise leading to weight loss, decrease the fat content in one’s liver to restore basic liver function. In cases where there has been severe damage, a person might have to undergo a liver transplant. The treatment plan should be indicated and based on the underlying cause of hepatic parenchymal disease and on the needs of each individual patient.
Complications of Hepatic Parenchymal Disease
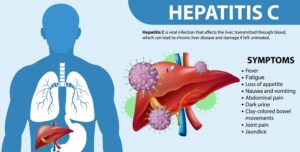
Untreated hepatic parenchymal disease may lead to several serious complications. Of all the possible complications, one of the most critical is cirrhosis; it is a condition whereby the liver becomes severely scarred and cannot function properly. Cirrhosis may be complicated by liver failure, a condition whereby the liver fails to carry out its necessary functions in an actual emergency. threatening life. Another complication is the development of primary liver cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma may develop, especially in the setting of chronic liver disease. Furthermore, hepatic parenchymal disease can evolve into portal hypertension. Knowing the complications schematically may help in understanding why early disease detection and treatment of hepatic parenchymal disease may be of much importance.
Prevention of Hepatic Parenchymal Disease
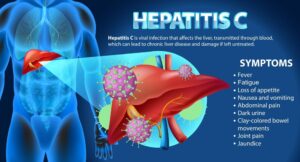
Prevention of hepatic parenchymal disease deals with avoiding the risks leading to liver damage. Optimal control by moderation or complete avoidance of alcohol in drinkers is necessary to avoid alcoholic liver disease. Diet and exercise for weight support can lessen the risk of the occurrence of non-alcoholic greasy liver sickness. Regular medical check-ups and liver function tests need to be done to recognize early hepatic parenchymal disease and have early prevention measures against its progression.
Diet and lifestyle modifications

A healthy diet and lifestyle would go a long way in managing hepatic parenchymal disease. The liver will be in good shape if the diet consists of plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. The intake of saturated fats, sugars, and processed foods has to be minor and, preferably low, for a person suffering from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Physical activity is also essential to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight and keeping the liver safe from damage. Avoiding the intake of alcohol and tobacco is a must, as they show a significant worsening impact on the liver. Such diet and lifestyle alterations could significantly change the prognosis of hepatic parenchymal disease patients.
Role of Drugs

Drugs may have a crucial role in treating hepatic parenchymal disease, especially when it is related to viral hepatitis or other predisposing factors. Patients with hepatitis B and C are generally provided with antivirals, which help decrease inflammation in their liver and offer a helping hand from further damage. In autoimmune liver diseases, patients may also be prescribed immunosuppressive drugs to suppress the attack of their immune system on the organ. Further medications for controlling pain, swelling, confusion, or other symptoms may be needed. One is required to have the best treatment of hepatic parenchymal disease by a health provider and follow the prescribed treatment plan.
Monitoring and follow-up care

hepatic parenchymal disease management Monitoring is a very critical aspect of the management. Hepatic parenchymal disease-diagnosed patients should have routine tests to check on the extent of liver functioning and how effective the treatment is. Imaging studies may also be repeated from time to time to monitor the state of the liver over the years. Consequently, patients should work with their providers to adapt plans to intervene as appropriate and report new symptoms and complications while they are still early. Follow-up care is instrumental to prevent hepatic parenchymal disease from degenerating; therefore, strict adherence to the recommended follow-up schedule is very crucial for a better prognosis.
Living with Hepatic Parenchymal Disease

The people living with hepatic parenchymal disease must adhere to their medications, attend occasional check-ups, and maintain a liver-friendly diet while keeping away from alcohol and keeping their weight in check to minimize liver stress. Emotional support through support groups or counseling to cope with living with a chronic liver condition really helps.