What Is Dorsalgia? Symptoms, causes, and remedies
What is drosalgia?
Dorsalgia is pain emanating from the back and may relate to the upper, middle, or lower regions. It may be due to severe strain of muscles, poor posture, abnormalities of the vertebral column, or other underlying pathological conditions. General symptoms include chronic backache, stiffness, and restricted movements.
Some of the important facts about dorsalgia are:
- Causes: muscle strain, herniated discs, poor posture
- Symptoms: sharp/dull pain in the back and restriction of movement.
- Diagnosis: physical examination and radiological investigations.
- Treatment: pain alleviation, physiotherapy, and modifications in lifestyle.
- Prevention: Exercise on a regular basis, maintaining posture, and making ergonomic changes.
Types of Dorsalgia
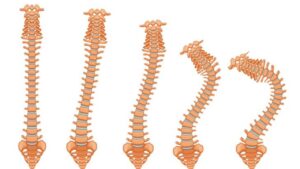
Dorsalgia encompasses different types depending upon the site of pain and origin.
The important types of dorsalgiea are:
- Cervical : Pain in the cervical region.
- Thoracic : Pain in the middle back.
- Lumbar : Low backache.
- Acute : Pain lasting for a short duration.
- Chronic : Pain present for a long period.
- Mechanical : Pain originating from mechanical injury.
- Inflammatory : Pain related to inflammatory conditions.
What are the symptoms of drosalgia?
The symptoms of dorsalgia vary according to the root cause and seriousness of the condition that affects daily activity and well-being.
Common signs and symptoms of dorsalgia include
- Back Pain: Mild or severe, and usually persistent
- Stiffness: An inability to move or bend the back
- Muscle Spasm: Sudden painful contractions of back muscles
- Numbness or Tingling: Numbness or tingling sensations in the back or legs
- Radiating pain: pain that radiates to the neck, shoulders, or legs.
What is the Cause of Dorsalgia?

Dorsalgia may be caused by one or several factors that impinge on the back muscles, spine, and tissues surrounding them. These causes, if known, aid in the management and prevention of the disorder.
The following are some of the key causes:
- Muscle strain: Overuse and jerking movements may cause strain to the back.
- Poor posture: Sitting and standing incorrectly strains the spine.
- Herniated discs: discs in the spine slip out of place and touch a nerve.
- OA: Degeneration of spinal joints causing pain.
- Spinal Stenosis: Narrowing of the spinal canal that pinches nerves.
- Trauma/Injury: Falls, accidents, or heavy lifting.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Disorders like ankylosing spondylitis affecting the spine.
Remedies for Dorsalgia

There are several remedies that may help ease dorsalgia or back pain. Rest and avoidance of activities that aggravate the pain are useful. Heat and cold therapy relieve discomfort and reduce swelling. Some mild stretches and exercises strengthen the back and enhance flexibility.
Following are some of the remedies that can help in managing dorsalgia or back pain:
- Rest and Avoid Strain: Give your back time to cure by avoiding activities that aggravate the pain.
- Heat and Cold Packs: Apply heat to loosen the muscles and ice to reduce inflammation.
- Light Exercises: Perform stretches and strengthening exercises to help build flexibility and support your back.
- Pain Relievers: Take over-the-counter medications to minimize pain temporarily.
- Good Posture: Maintain proper posture with supportive furniture to reduce strain on your back.
What are the Best Treatments for Dorsalgia?

Dorsalgia is treated using proper pain relief and movement enhancement techniques.
Following are some of the best treatments for dorsalgia:
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to help strengthen the muscles of the back and also exercise to improve posture.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Heat or ice packs may be applied to the aching area to reduce any pain and inflammation.
- Chiropractic Care: Adjustments to the spine will help alleviate pain.
- Lifestyle Changes: Keeping weight down, exercising regularly, and ergonomic changes.
- Surgery: The worst cases may ultimately require surgery.
How is Dorsalgia Treated?

The treatments for dorsalgia are numerous and aim at pain reduction and restoration of function.
Here are some common treatment modalities available for dorsalgia:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Periods of rest balanced by gentle activities to avoid exacerbation of symptoms.
- Pain Medication: Over-the-counter and prescription medications can include NSAIDs.
- Physical Therapy: Personalized exercises and stretches to strengthen the back.
- Manual Therapy: This can include techniques such as chiropractic adjustments or massage.
- Heat and Ice Application: Results in vasoconstriction and the alleviation of swelling that soothes muscles.
- Correction of Posture: Ergonomic adjustments at work and home.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture and yoga for pain relief and relaxation.
Risks and Side Effects of Dorsalgia Treatments Explained

In treating dorsalgia, there is a need to create awareness of the dangers and side effects likely to be associated with any of the various therapies. Drugs or pain relievers can have side effects that include gastrointestinal problems, dizziness, or dependence when taken over a long period. Physical therapy is usually harmless, but sometimes it may lead to increased pain if the exercises are not well performed.
Some of the common ones are listed as follows:
- Medication Side Effects: Pain relievers can cause stomach upset, dizziness, or dependency.
- Chiropractic Adjustments: Spinal adjustments rarely may cause nerve irritation or minor trauma.
- Surgery Risks: infection, nerve damage, or incomplete pain relief.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture or massage may lead to temporary soreness or bruising.
Dorsalgia Self-Care Tips
Self-care in managing dorsalgia can make quite a difference in comfort by easing your back pain. Keep active with the help of light exercises such as walking and stretching. Such forms of exercise will enable your muscles to be flexible and strong. Good posture—while sitting, standing, and working—can ward off extra strain on your back.
Self-care for dorsalgia is simple and can be carried out with ease; the steps are outlined below:
- Keep Active: Dorsalgia treats mild exercises like walking or stretching to maintain the muscles of the back strong.
- Maintain Good Posture: The need to sit and stand straight with ease, as this avoids straining the back.
- Heat and Ice Application: The application of heat keeps the muscles relaxed; on the other hand, ice reduces swelling and reduces pain.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting: Avoid lifting heavy objects that will increase your tendency towards dorsalgia.
Medical Tests for Dorsalgia
Many medical tests doctors prescribe for diagnosing dorsalgia and finding the very root of back pain. Common tests include physical examinations, X-rays for bones, and MRI or CT scans for muscle and nerve details. Blood tests and nerve tests can also be carried out to locate the underlying problems.
Following are some of the common tests:
- Physical Examination: Physicians examine your back, movement, and areas of pain.
- X-rays: Pictures of your spine reveal bone conditions such as fractures or arthritis.
- MRI or CT scans: These scans would present detailed pictures of muscles, discs, and nerves.
- Blood tests: to identify infections or inflammatory diseases.
- Nerve Tests: A procedure that measures how well your nerves are functioning, especially in cases where pain extends to arms or legs.
Risk factors for dysalgia

Back pain or dorsalgia may be related to various risk factors, such as poor posture—for example, slouching—puts extra strain on your spine; lack of habitual exercise diminishes your back muscles, therefore increasing the level of pain. Incorrect lifting of heavy weights may strain your back; wear and tear on spinal disks as you age can result in herniated disks.
These include:
- Poor Posture: Slouching while sitting or standing puts extra pressure on the spine.
- Not exercising enough: weak back and core muscles lead to dorsalgia.
- Heavy Lifting: Poor lifting techniques can strain your back muscles.
- Age: It is common to have back pain as people get older.
- Obesity: Extra weight in the body adds extra stress on the spine.
- Stress: Tension can cause muscle tightness, leading to dorsalgia.




